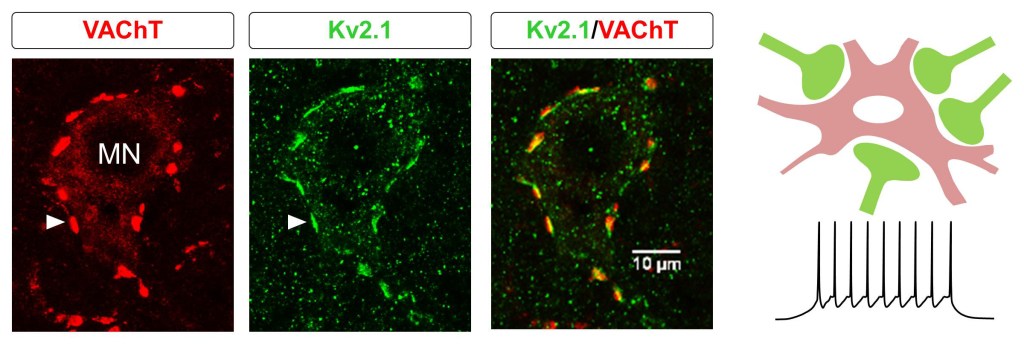
C-boutons are prominent modulatory synapses located on the soma and proximal dendrites of motoneurons. For a long time, their origin was unknown, however, Laskaro Zagoraiou (Athens Academy) and Gareth Miles (St Andrews) discovered that a small subset of cholinergic neurons called V0c interneurons, which can be identified based on the expression of the Pitx2 transcription factor and give rise to all of the C bouton synapses in the spinal cord (Zagoraiou et al., 2009).
Zagoraiou and Miles have continued to study the C bouton system in their independent Labs and have advanced our understanding of how this prominent neuromodulatory synapse controls motoneuron function in health and disease. Generally speaking, acetylcholine released by V0c interneurons at their C bouton synapses increase motoneuron and locomotor output by activating M2 muscarinic receptors to modulate the activity of Kv2.1 channels (Nascimento et al, 2020).
A novel signaling peptide discovered at C bouton synapses!
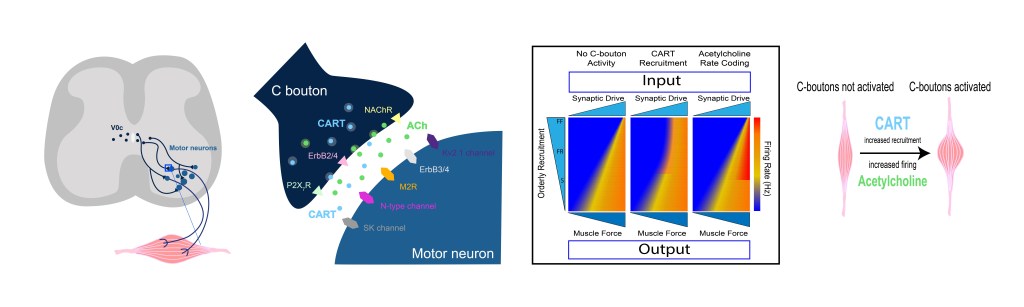
Recent work in the Zagoraiou Lab discovered that V0c interneurons and their C bouton synapses are enriched in a neuropeptide encoded by the Cocaine and Amphetamine Related Transcript (CART), with its deletion leading to impaired ability to perform motor tasks that require maximal muscle force to be exerted. I was fortunate to have the opportunity to contribute to this project and study what affect, if any CART might exert on motoneuron excitability.
Using whole cell patch clamp electrophysiology, I discovered that CART increases the recruitment of fast type motoneurons, which are important for the generation of movements that require large amounts of muscle force. In contrast, muscarine, a drug that activates acetylcholine receptors, increases the firing rates of this same type of motoneuron, and did not alter their recruitment. Thus, two neuromodulators that are present at the same synapse can act to increase motor output by acting through distinct, but parallel mechanisms.
This work was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
V0c control of breathing circuits
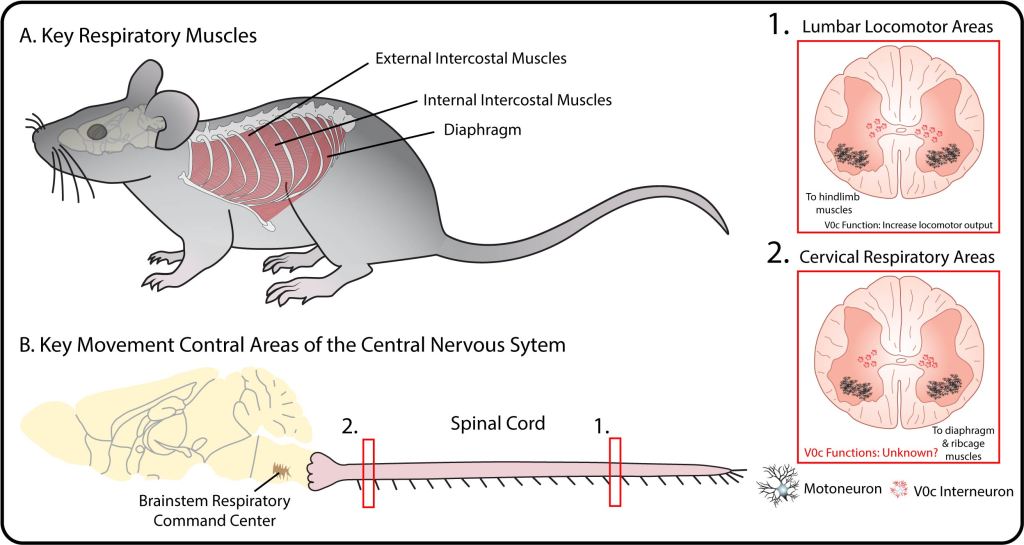
V0c interneurons and C bouton synapses can also be found throughout the nervous system (Rozani, et al., 2019), however their diverse functions are not known. We have recently begun to study some of these other functions.
Breathing is undeniably one of the more important motor functions that we must perform. It must persist from the first breath that we take when we are born and continue until we die. Breathing also must be adapted to meet constantly changing metabolic demands. Therefore, the underlying neural networks that generate breathing must not only be robust, but also adaptable.
We recently uncovered a novel spinal mechanism that enhances breathing during hypercapnic states, such as exercise. In collaboration with Polyxeni Philippidou (Case Western Reserve University), we showed that V0c interneurons projecting to phrenic motoneurons amplify breathing through M2 muscarinic receptors. Interestingly, this pathway is anatomically-distinct from that involved in limb control, suggesting specialized spinal circuits for motor amplification.
This work was recently published in Cell Reports.
Outputs
Research Articles
Lin, M.*, Calabrese, G.B.*, Incognito, A.V., Moore, M.T., Agarwal, A., Wilson, R.J., Zagoraiou, L., Sharples, S.A.+, Miles, G.B.+, Philippidou, P. +. (2025). A cholinergic spinal pathway for the adaptive control of breathing. Cell Reports. 44(8). 116078. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116078. + Corresponding Authors
Eleftheriadis, P.E.*, Pothakos, K.*, Sharples., S.A., Apostolou, P., Mina, M., Tetringa, E., Miles, G.B., and Zagoraiou, L. Peptidergic modulation of motor neuron output via CART signalling at C bouton synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 120 (39). e2300348120. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2300348120.
Abstracts and Conferences
Eleftheriadis, P.E., Pothakos, K., Sharples., S.A., Apostolou, P., Mina, M., Tetrigga, E., Miles, G.B., and Zagoraiou, L*. CART modulation of motor neuron output at C bouton synapses. Motor Control: Spinal Circuits and Beyond, St Andrews, United Kingdom, June 2023.
Calabrese, G.B*., Broadhead, M.J., Incognito, A.V., Motherwell, L., Wilson, R.J., Sharples, S.A., and Miles, G.B. Spinal cholinergic modulation of spinal circuits for breathing. Motor Control: Spinal Circuits & Beyond. St Andrews, UK. June 2023.
Calabrese, G.B.*, Broadhead, M.J., Motherwell, L., Sharples, S.A., and Miles, G.B. Cholinergic modulation of respiratory-related motor output. Society for Neuroscience. San Diego, CA, USA. Nov 2022.
Calabrese, G.B.*, Broadhead, M.J., Motherwell, L., Sharples, S.A., and Miles, G.B. Cholinergic modulation of respiratory-related motor output. International Motoneuron Society Meeting. Banff, AB, Canada, June 2022.
Funding


